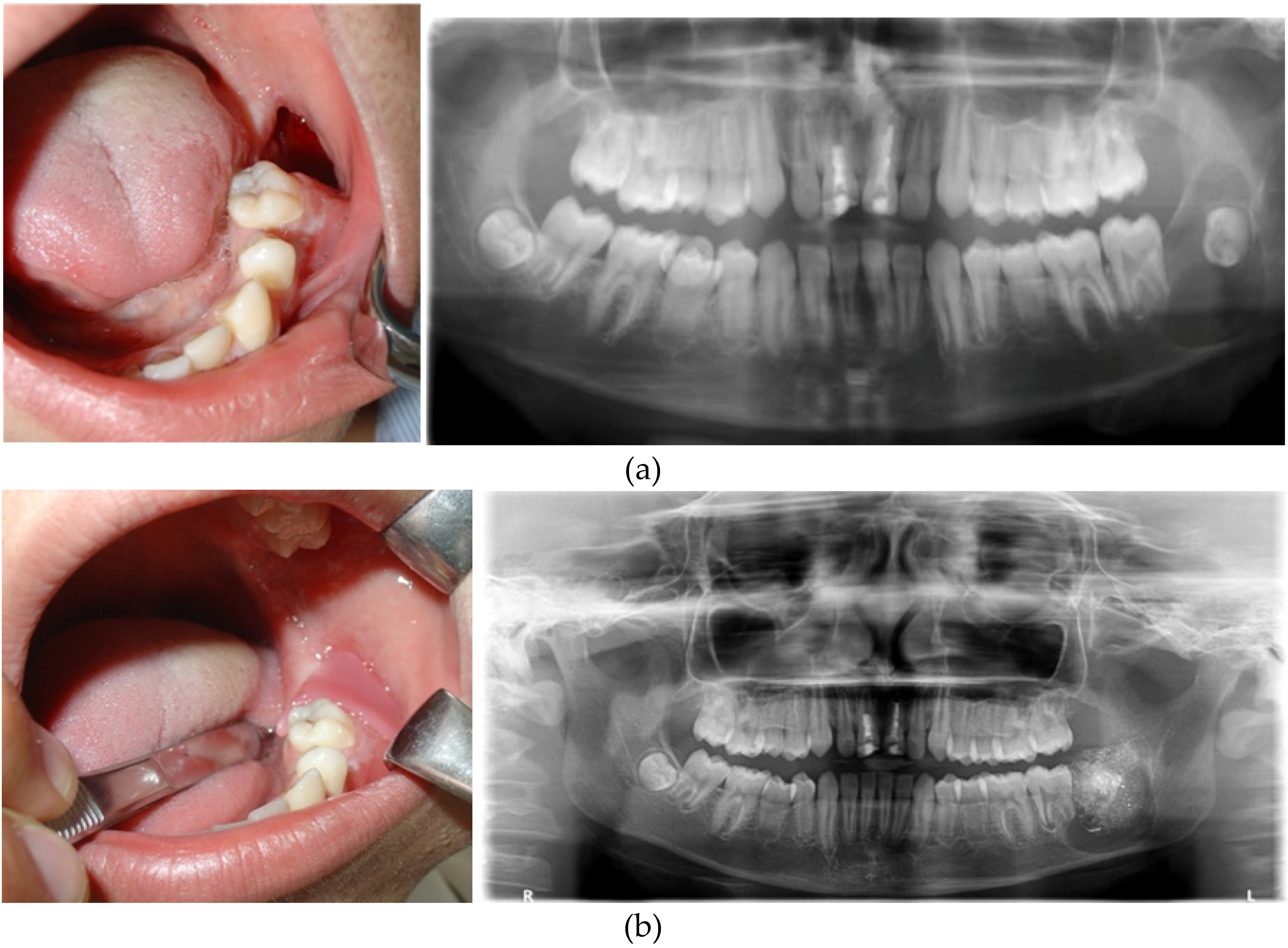
Treatment Options:
- Observation: Some small and asymptomatic lesions may be monitored without immediate intervention.
- Observation: Surgical Excision: Complete removal of the tumor or cyst, ensuring minimal damage to surrounding structures.
- Marsupialization: Marsupialization: Creating an opening to allow drainage and shrinkage of the cyst before complete removal.
- Enucleation: Removal of the entire lesion, often used for cysts.
Reconstructive Surgery:
- For larger lesions or those affecting jaw structure, reconstructive surgery may be necessary.
- Techniques like bone grafting may be employed to restore jaw integrity.
Orthodontic Intervention:
- Benign lesions affecting tooth eruption may require orthodontic treatment to reposition teeth.
Follow-up and Monitoring:
- Regular follow-up to ensure complete healing and to address any potential recurrence.
- Monitoring of adjacent teeth and bone health.
Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Collaboration with oral and maxillofacial surgeons, orthodontists, and pathologists for comprehensive care.
- In cases where lesions are associated with impacted teeth, coordination with an oral surgeon or orthodontist is essential.
Patient Education:
- Educating patients about the nature of their condition, treatment options, and the importance of follow-up care.
- Emphasizing the benign nature of most jaw tumors and cysts, alleviating anxiety.
Management of benign tumors and cysts of the jaw requires a thorough understanding of the specific condition, careful planning, and a collaborative effort among healthcare professionals. Personalized treatment plans consider the patient's overall health, the nature of the lesion, and the impact on oral function and aesthetics.